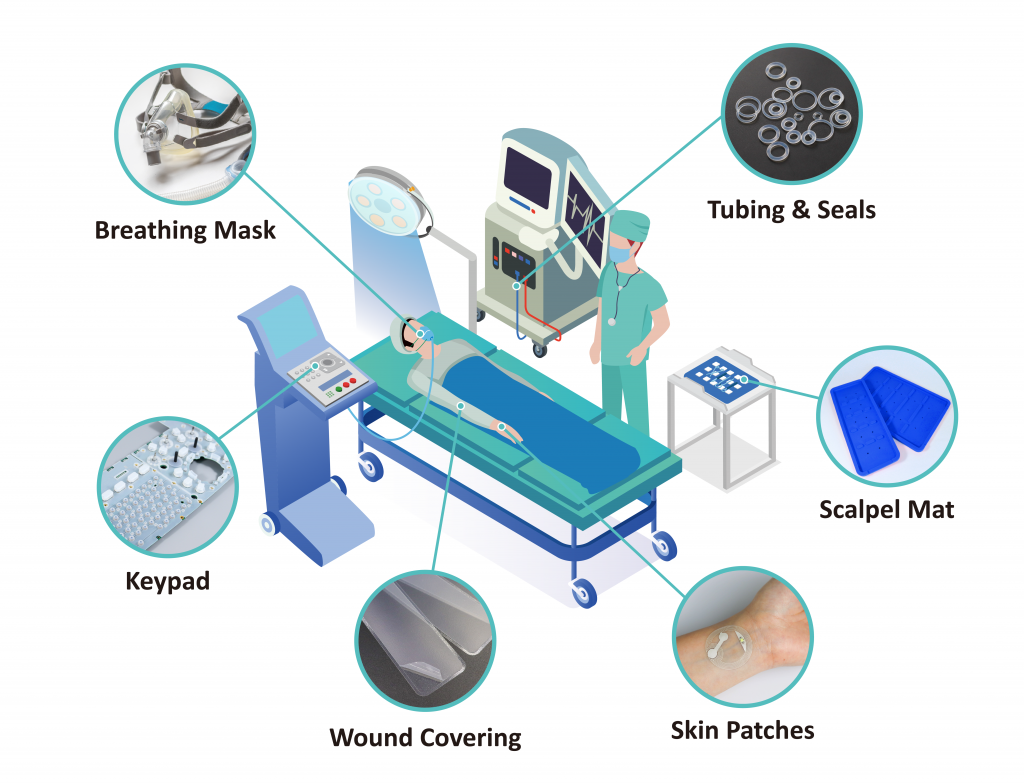
In the dynamic world of healthcare and medical device manufacturing, medical silicone rubber stands as an indispensable material. It is chosen for its unparalleled purity. Critically, it offers superior biocompatibility. This means it safely interacts with living tissue without adverse reactions.
This unique elastomer adheres to stringent global standards. These include USP Class VI and ISO 10993. It is often backed by FDA approval. This ensures its suitability for a vast array of applications. Examples include catheters, tubing, prosthetics, and implantable devices.
Its robust properties are key. These include exceptional thermal stability, flexibility, chemical inertness, and sterilizability. Such features enable the creation of safer, more durable, and highly effective medical solutions. This overview explores medical silicone rubber’s vital role. It is not merely a component. It acts as a cornerstone, enabling innovation across the entire healthcare landscape. Continuous advancements in cutting-edge research push its capabilities further. This enhances patient outcomes worldwide.
What Is Medical Silicone Rubber?
In the medical and healthcare fields, medical silicone rubber is a crucial material. It’s a synthetic polymer, well-known for its flexibility and stability. This material is specifically designed for medical uses. It provides a good balance of performance and safety.
This type of silicone undergoes strict testing. This ensures it meets all healthcare standards. Its biocompatibility means it can safely touch human tissue. It does not cause irritation.
Certification of Material and Finished Products
Medical Silicone Materials (Raw Compounds) certification:
Navigating the world of medical silicone is complex, with stringent regulations governing both raw materials and finished medical devices to ensure patient safety and product efficacy.
- ISO 10993 (Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices): An international series of standards providing a framework for the biological evaluation of medical devices. For materials, the focus is often on:
- ISO 10993-1: Biological evaluation and testing within a risk management process.
- ISO 10993-5: In vitro cytotoxicity testing.
- ISO 10993-10: Tests for skin sensitization and irritation.
- ISO 10993-11: Tests for systemic toxicity.
- For long-term implants, ISO 10993-6 (local effects after implantation) and ISO 10993-3 (genotoxicity) may also be required.
- USP Class VI (United States Pharmacopeia Class VI): This is the most common and stringent biological reactivity test in the U.S. It assesses whether a material causes toxicity, irritation, or allergic reactions upon contact with living tissue. Class VI is the highest level, typically requiring a series of tests including hemolysis, cytotoxicity, sensitization, irritation, and in vivo implantation (short-term and long-term).
- FDA 21 CFR 177.2600: This U.S. FDA regulation outlines safety requirements for rubber articles intended for repeated use in food contact, but it’s often referenced in medical applications for material purity and extractable limits.
- REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals): An EU regulation managing and restricting chemical use to ensure safety. Medical silicone materials must comply with REACH, limiting harmful substances like phthalates and heavy metals.
- RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances): An EU directive restricting hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment; some medical device components may also be affected.
Medical Silicone Products (Finished Devices) certification:
- ISO 13485 (Medical Devices – Quality Management Systems):** This is a global standard. It’s for quality management systems. It applies specifically to the medical device industry. Certification shows a manufacturer’s system meets international requirements. This covers designing, developing, producing, installing, and servicing medical devices.
- FDA Approval/Clearance (U.S.):** Medical devices need FDA approval for the U.S. market. This involves either Premarket Approval (PMA) or Premarket Notification (510(k)). Manufacturers submit detailed technical documents. These include material biocompatibility data. ISO 10993 and USP Class VI are often referenced. Design validation, manufacturing controls, and clinical data are also part of this.
- CE Marking (Conformité Européenne):** This is a mandatory mark. It’s for medical devices sold in the EU market. Manufacturers must complete a conformity assessment. The procedure depends on the device’s risk class. This process proves compliance with the EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR, EU 2017/745). It confirms essential safety and performance requirements are met.
Application according to ISO 10993
| Standard | e.g., |
| Surface Devices (Contact with intact skin or mucous membranes): These devices generally require testing for immediate local effects. | Electrodes / Wearable Sensors / Wound Dressings (non-invasive) / External Prosthetics / Breathing Tubes/Masks / Endoscopes / Urinary Catheters (external parts) |
| External Communicating Devices (Indirect or direct contact with internal body environment): These devices have a pathway to internal body fluids or tissues, necessitating a broader range of tests. | Blood Path, Indirect: IV Administration Sets / Blood Bags/Storage Systems / Dialysis Equipment Tissue/Bone/Dentin Communicating: Surgical Drains / Wound Dressings (invasive) / Dental Fillings Circulating Blood Contact: Intravascular Catheters / Heart Valves / Blood Pumps / Oxygenators |
| Implant Devices (Placed within the body): These devices carry the highest risk due to long-term internal contact and require the most comprehensive biological evaluations. | Bone Contact: Orthopedic Implants / Dental Implants Tissue and/or Bone Contact: Breast Implants / Pacemakers / Defibrillators / Surgical Meshes / Drug Delivery Implants / Neurological Stimulators Blood Contact (Long-term Implants): Vascular Grafts / Stents |
Medical Silicone for Long-Term Implantation
When navigating the world of medical silicone, it’s crucial to understand the distinct certification pathways for the raw material and the finished medical device. Both are subject to stringent regulations to ensure patient safety and product efficacy.
These material suppliers typically provide detailed certifications and supporting documents, including:
- USP Class VI Reports: Confirming the material’s biological reactivity meets the highest standards.
- ISO 10993 Series Test Data: Especially for long-term implantation (e.g., ISO 10993-6 for local effects after implantation, and other relevant tests for systemic toxicity, sensitization, etc.).
- Master File (MAF) or Drug Master File (DMF) Support: Material information submitted to regulatory bodies (like the U.S. FDA) for easy reference by medical device manufacturers when seeking product approval.
- ISO 13485 Quality Management System Certification: While primarily for medical device manufacturers, leading material suppliers often implement similar quality management standards in their medical-grade silicone production facilities, sometimes even in cleanroom environments.
Here are some of the major global manufacturers that supply medical-grade silicone materials for permanent implantation, along with their typical product lines or grades:
Major Global Manufacturers and Typical Grades for Permanent Implant-Grade Medical Silicone
- NuSil Technology LLC (An Avantor Company): NuSil is a global leader specializing in high-performance silicone materials for medical and life science applications. They have extensive product portfolios and deep expertise in biomedical-grade silicones, especially for long-term implant applications.
- Typical Grades/Product Lines: NuSil™ Implant Line (a comprehensive series for implants), NuSil™ Med-X® Series (certain high-purity grades), NuSil™ DH series (high-purity LSR/HCR grades), NuSil™ Silicone Gels (for filling or soft tissue interfaces).
- DuPont Liveo™: DuPont’s Liveo™ brand offers silicone elastomers specifically for healthcare, including Q7 biomedical-grade elastomers that comply with ISO 10993 and USP Class VI, suitable for Class III medical devices or long-term (over 30 days) implant applications.
- Typical Grades/Product Lines: Liveo™ Q7 Biomedical Grade Elastomers, Liveo™ QP1-2XX LSR Series (LSR grades with excellent biocompatibility).
- Elkem Silicones: Elkem is a leading global silicone producer. Their Silbione™ series of medical-grade silicones is widely used in medical devices, including long-term implantable biomedical applications, meeting relevant biocompatibility standards.
- Typical Grades/Product Lines: Silbione™ Biomedical Series (high-purity medical-grade silicones, including HCR, LSR, RTV, specifically designed for long-term implants).
- Wacker Chemie AG: Wacker is a well-known global silicone manufacturer. Their product range includes specialty silicones for medical and pharmaceutical industries, suitable for various implants.
- Typical Grades/Product Lines: SILPURAN® Series (Wacker’s high-purity silicone series for medical and pharma applications, with specific grades designed for implantable devices), ELASTOSIL® Series (certain high-purity grades).
- Momentive Performance Materials: Momentive provides high-performance silicone solutions, including various products for the healthcare sector.
- Typical Grades/Product Lines: ReliaSil™ UV Product Line (UV-curable elastomers, positioned for next-generation long-term implants), Silopren™ LSR Series (certain medical-grade models).
Conclusion
Sure, here’s that paragraph again, but with shorter sentences:
In summary, medical silicone is indispensable in healthcare. It’s valued for its unique blend of biocompatibility, versatility, and long-term stability. This material sees widespread use. It’s found in simple tubing and complex permanent implants. Its application is underpinned by rigorous adherence to global standards. These include ISO 10993 and USP Class VI. Regulatory approvals from bodies like the FDA are also crucial. Specialized manufacturers lead the market. They provide highly pure grades. These are tailored for critical applications. Medical technology continues to advance. The ongoing innovation in silicone materials will remain fundamental. This helps develop safer, more effective, and groundbreaking healthcare solutions worldwide.